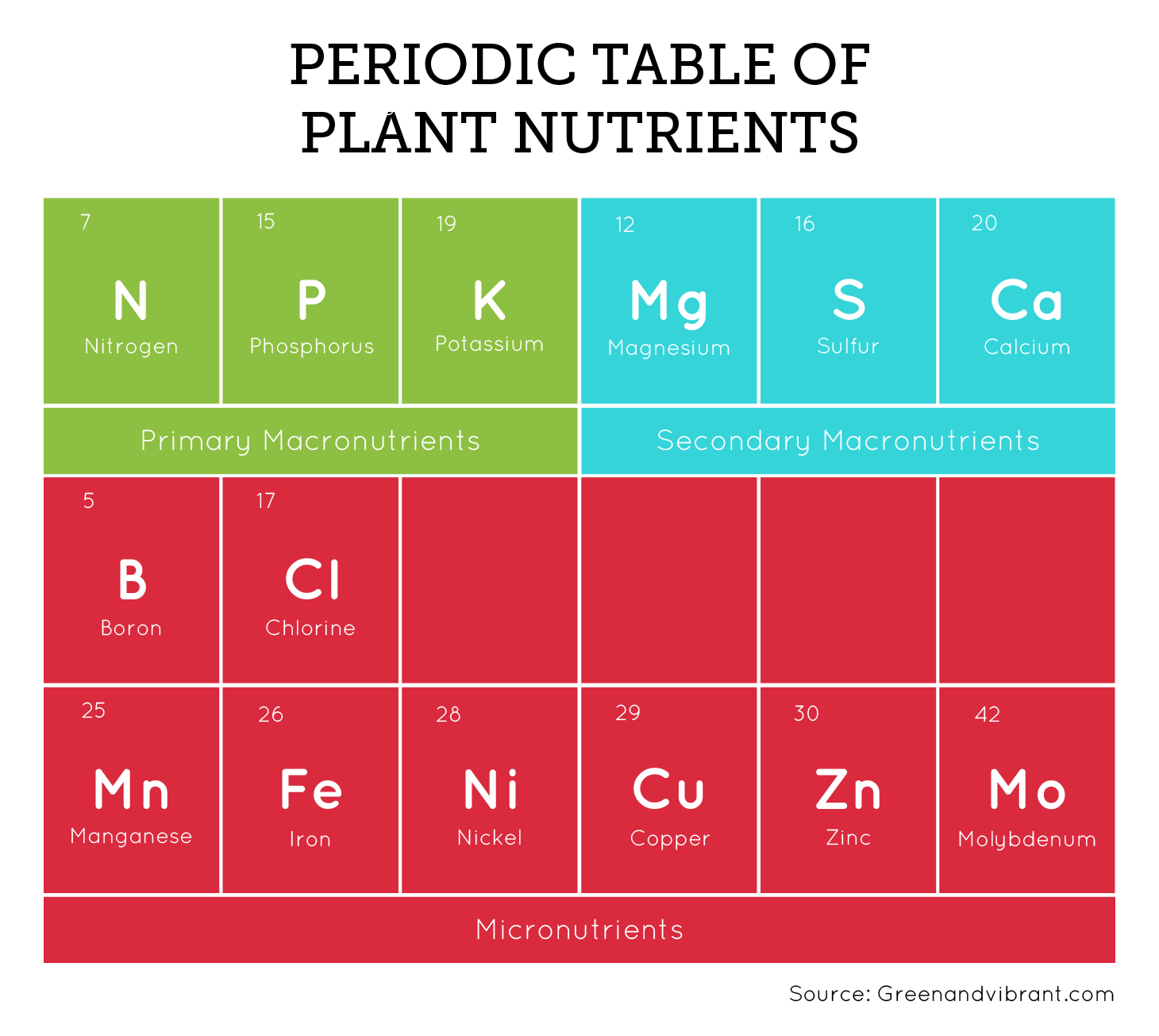
Essential Nutrients for Hydroponic Gardening Success
Introduction
Hydroponics, the practice of growing plants in a water-based, nutrient-rich solution, eliminates the need for soil. This innovative technique has surged in popularity, particularly in areas with limited arable land. The effectiveness of hydroponic gardening, however, relies on maintaining a precise balance of nutrients. In this article, we explore the critical nutrients necessary for hydroponic systems and their roles in ensuring healthy plant development.
1. Nitrogen (N)
Role in Plant Growth
Nitrogen is essential for the synthesis of chlorophyll, which plants use during photosynthesis. It also plays a significant role in the production of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins. In hydroponic systems, nitrogen is often provided as nitrate.
Signs of Deficiency or Excess
- Deficiency: Stunted growth, yellowing of older leaves (chlorosis).
- Excess: Dark green foliage, delayed flowering due to excessive vegetative growth.
2. Phosphorus (P)
Role in Plant Growth
Phosphorus is crucial for energy transfer in plants and is key to the formation of DNA, RNA, and ATP. It supports root development and promotes flowering.
Signs of Deficiency or Excess
- Deficiency: Dark green or purplish leaves, stunted growth, small root systems.
- Excess: May cause iron and zinc deficiencies.
3. Potassium (K)
Role in Plant Growth
Potassium helps regulate photosynthesis, nutrient transport, and enzyme activation. It's vital for water regulation and disease resistance.
Signs of Deficiency or Excess
- Deficiency: Yellowing or browning of leaf edges, weak stems.
- Excess: Can cause deficiencies in calcium and magnesium.
4. Calcium (Ca)
Role in Plant Growth
Calcium is integral to cell wall structure and growth, helping maintain plant rigidity and resistance to pathogens.
Signs of Deficiency or Excess
- Deficiency: Deformed new leaves, root tip dieback.
- Excess: Rare, but may interfere with uptake of other nutrients.
5. Magnesium (Mg)
Role in Plant Growth
Magnesium is the central element in chlorophyll and is essential for energy production and enzyme activation.
Signs of Deficiency or Excess
- Deficiency: Yellowing between leaf veins, curling leaves.
- Excess: May disrupt calcium absorption.
6. Sulfur (S)
Role in Plant Growth
Sulfur supports the production of amino acids, vitamins, and enzymes. It enhances flavor and aroma in edible crops.
Signs of Deficiency or Excess
- Deficiency: Pale or yellow young leaves, reduced growth.
- Excess: Rare, but can cause leaf tip burn.
7. Microelements
Role in Plant Growth
Microelements such as Iron (Fe), Manganese (Mn), Boron (B), Copper (Cu), Zinc (Zn), Molybdenum (Mo), and Chlorine (Cl) are needed in small quantities but are vital for enzymatic reactions and physiological functions.
Signs of Deficiency or Excess
Each microelement shows specific symptoms; for example, iron deficiency causes interveinal chlorosis, while excesses may lead to toxicity or imbalance in other nutrients.
Conclusion
Balanced nutrition is the cornerstone of successful hydroponic gardening. Monitoring and adjusting the nutrient solution regularly helps prevent both deficiencies and toxicities. Whether you're a beginner or a seasoned grower, understanding and managing these essential nutrients is key to cultivating healthy, productive plants in a soil-free environment.
Note:
Always follow the guidelines provided by nutrient manufacturers and consider the unique requirements of your specific plant varieties. Nutrient needs may vary depending on plant species, growth stage, and environmental conditions.